Fuel for Growth: How to Create Effective Employee Development Plans

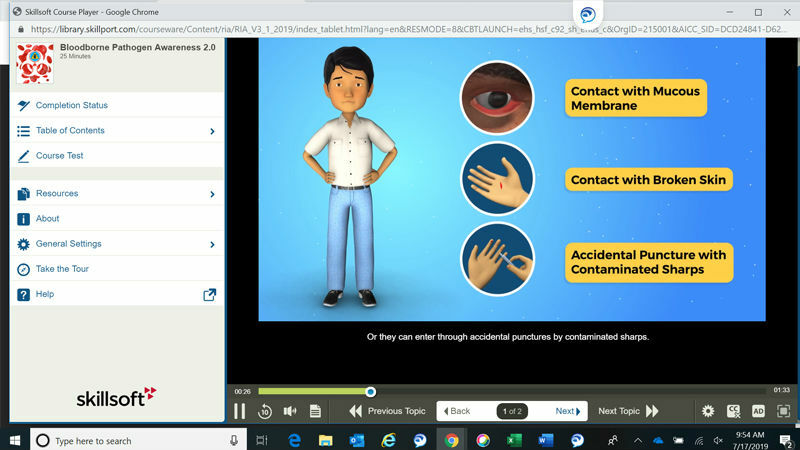
According to OSHA, bloodborne pathogens (BBPS) are pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to, hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). To protect workers from severe or life-threatening illnesses arising from contact with BBPS, OSHA created standards that prescribe safeguards against the hazards posed by BBPS. In 2001, these standards became effective. For the complete set of requirements, read Title 29 of the Code of Federal Regulations at 29 CFR 1910.1030.
OSHA’s standards address occupational exposure to BBPS. OSHA defines occupational exposure as reasonably anticipated skin, eye, mucous membrane, or parenteral contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials that may result from the performance of an employee’s duties. It’s the employer’s responsibility to protect employees who have the potential for exposure to BBPS as they perform tasks associated with their job.
The Center for Disease Control (CDC) estimates that 5.6 million employees are at risk of occupational exposure to bloodborne pathogens. Maintaining a safe and healthful workplace is essential to both employers and employees. Although healthcare workers are the most likely to be exposed, employees working other types of jobs are also at risk. These workers include custodians, emergency responders and law enforcement officers. Office, retail, and restaurant workers also have the potential for exposure due to workplace accidents.
In general, the BBPS standard requires employers to:
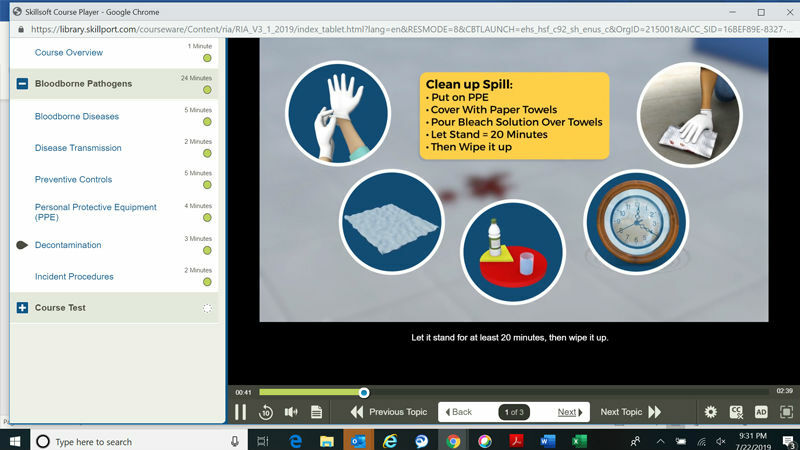
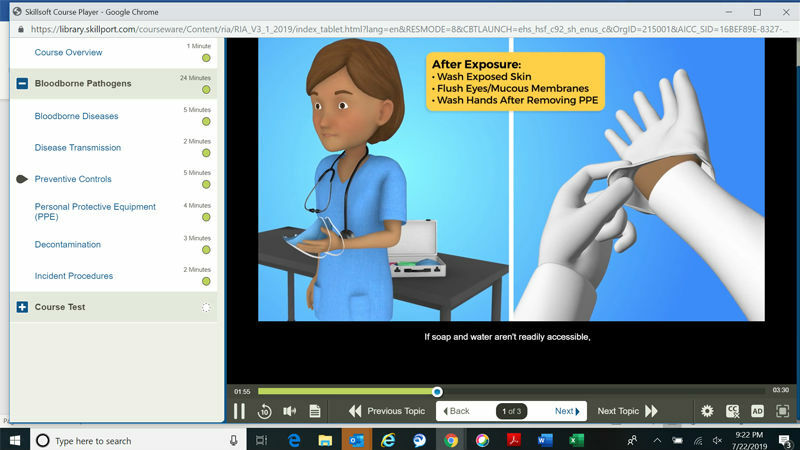
Learn more with the Quick Reference Guide to the Bloodborne Pathogens Standard and Occupations Affected by Bloodborne Infectious Diseases
In addition to protecting workers, a well planned and executed BBPS program provides the foundation for successful audit and inspection results. OSHA can discover violations during programmed/regularly scheduled inspections or when investigating imminent dangers, fatalities and catastrophes or complaints.
OSHA’s five most commonly cited sections of the BBPS regulations are:
The following case provides a good illustration. In 2016, OSHA received a complaint alleging employee exposure to blood and other potentially infectious bodily fluids while handling packages labeled as containing biological infectious materials. OSHA’s inspection documented willful and serious violations related to the employer’s failure to have an implemented written exposure control plan and a failure to train workers on bloodborne pathogen hazards and protections. The employer had also failed to provide appropriately sized gloves, had not completed an exposure determination, and had failed to offer potentially exposed employees the Hepatitis B vaccine. The proposed penalties totaled $342,059.
Skillsoft’s Bloodborne Pathogen Awareness course is one of the top three environmental, health and safety titles accessed by Skillsoft learners worldwide. If desired, employers can supplement the online course by combining the online content with non-web-based training. Companies can also add a customization package to the Skillsoft online course. Customization can include a custom course title, access to an employer’s bloodborne pathogens exposure control plan, localization and the addition of an employer’s qualified trainer contact information.
Skillsoft offers the following BBP training courses:
Allison von Gruenigen is a Compliance Solutions Consultant at Skillsoft.
We will email when we make a new post in your interest area.

